Reactive silanes (EU) can be used in multiple applications to enhance the performance of coatings. They can improve adhesion to inorganic substrates, provide crosslinking, improve pigment dispersion, improve hydrophobicity and scavenge moisture. A silane (EU) that contains at least one carbon silicon bond (CH3 – Si -) is called an organosilane (EU).Reactive silane is the term used to define compounds that have a trialkoxysilyl group and an alkyl group (R) containing a reactive constituent.
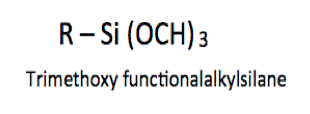 The trialkoxy silanes that are discussed in this article are those that contain primarily trimethoxy (EU) groups, as these molecules are the most widely used to enhance coating performance in a wide variety of applications, as follows:
The trialkoxy silanes that are discussed in this article are those that contain primarily trimethoxy (EU) groups, as these molecules are the most widely used to enhance coating performance in a wide variety of applications, as follows:
- Adhesion Promoter (EU)– Silanes, when added to paints, can enhance adhesion to inorganic surfaces including metals and glass.
- Coupling Agent (EU) – Silanes are used for coupling organic polymers to inorganic materials, including pigments and fillers.
- Crosslinking Agent (EU) – Selective organofunctional alkoxysilanes can react with organic polymers to provide a trialkoxysilyl group into the polymer backbone. In turn, the silane can then react with moisture to crosslink and form a three-dimensional siloxane cross-linked structure.
- Dispersing Agent (EU) – Used to improve the hydrophobicity of inorganic pigments, flow and the ability to be dispersed in organic polymers and solvents.
- Moisture Scavenger (EU) – In moisture sensitive formulations, the three alkoxysilane groups can scavenge water by reacting with moisture to form alcohol molecules.
To read the full article about Reactive Silanes for Enhancement of Coating Performance, click here.

